NATIONAL AERONAUTICS AND SPACE ADMINISTRATION
INSTITUTIONS/ORGANIZATION: GLOBAL INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
Global IT Los Angeles USA and The University of Global IT Naga City Cam Sur Philippines, are privately owned / School, family operated, managed IT and Cloud company. Global IT has specialized in IT Cloud operations since 2000 and virtualization since 2004. All Global IT staff and technicians are certified, courteous, prompt and professional.
arielmillanesagawajr1990nasa
COMTEQ will be the leader in the use of real-work environment as an effective training method in developing world class Filipino I.T. professionals nationwide.
OUR MISSION
We commit ourselves to continuously develop curricula and training methods that will fully satisfy the recent and anticipated training needs of Filipino students in the fast-advancing Information Technology industry.
OUR PRODUCTS
Our products are graduates of information technology and business courses, electronics and computer technologists, and highly-trained tourism workers which impart high-levels of skills, values-orientation, good communication and presentation abilities, and good command of the English language.
OUR TRAINING METHOD
In addition to theoretical learning in lecture rooms, COMTEQ maintains on-the-job training facilities in-house and employs a Dualized mode of training to provide students with actual training in real-work environment. Members of the faculty handling major subjects are 90% industry-based to ensure up-to-date and high-quality education. The students are molded by: a) providing them the necessary hands-on skills training in an actual shop; b) teaching them the values that successful individuals must possess; and c) developing their personalities and English communication skills.
CORPORATE VALUES
COMTEQ College is built around a set of core values:
Continual Improvement: We continually improve our facilities, course contents, teaching methods, and equipment, to ensure that our students keep up with the latest technological advances.
On-The-Job Training Emphasis: We place a high value in the use of on-the-job training, as the primary medium for imparting technical competence.
Modern Modes of Instruction: We believe that learning is a two-way street, thus, we actively promote modern participatory methods of instruction as tools for enhancing confidence levels and subject retention in our students.
Total quality education: We impart Filipino values in each of our students, a sense of social responsibility, positive attitude, and English communications skills to allow them to utilize their technical proficiency to the fullest.
Excellence: We ensure technical excellence in our graduates by providing them with the best mix of theoretical instruction and intensive on-the-job training at our in-house facilities.
Quality Service: We ensure quality service in an atmosphere of harmony through an empowered staff, and by instilling in our staff and students alike, the positive traits of mutual respect and cooperation.
Certificate Of Program Registration (COPR) No. : 1003072129
Course Description
The COMPUTER HARDWARE SERVICING NC II Qualification consists of competencies that must be possessed by a trainee to enable to diagnose and troubleshoot problems in personal computer systems, software, replace parts and get the system back to normal operation.
COMPETENCY REQUIREMENTS
BASIC COMPETENCIES
Participate in workplace communication
Work in a team environment
Practice career professionalism
Practice occupational health and safety procedures
COMMON COMPETENCIES
Apply quality standards
Perform computer operations
Perform mensuration and calculation
Prepare and interpret technical drawing
Use hand tools
Terminate and connect electrical wiring and electronic circuits
CORE COMPETENCIES
Install computer systems and networks
Diagnose and troubleshoot computer systems
Configure computer systems and networks
Maintain computer systems and networks
A person who has achieved this Qualification is competent to be:
Computer Service Technician
Computer Repairman
For more details: Click on it->http://www.comteq.edu.ph/portal/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=1:about-us&catid=8&Itemid=110&showall=1&limitstart=
Click->https://www.facebook.com/pages/global-IT-naga-city/108415079210324
Click->https://www.edukasyon.ph/schools/global-site-for-it-studies-naga-city
Click->https://tesdacourse.com/Global-Site-for-IT-Studies-Inc---Naga-1730.html
Click->https://globalit.com/
COMPUTER SPECIALIST RULES:
a.) Always wear Rubber Shoes Only
b.) Log off and/or turn it off Before Troubleshooting.
c.) Always Push and Pull a computer cable connector on it's owned Handle Connector.
d.) Always wear Electrostatic Discharge (ESD IEEE Tool) Before Troubleshooting.
e.) Keep away any Liquid, Water / E.g...
COMPUTER HARDWARE SERVICING:
OPERATING SYSTEM (OS), DRIVER PACK SOLUTION, UTILITY / MICROSOFT OFFICE COMPUTER PROGRAM (SOFTWARE/APPLICATION) INSTALLATION:
NETWORKING:
*) Windows Firewall.
*) DNS.
*) Port.
*) IP/E.g...
*) Test Print
*) CCTV (IP + Analogue Cameras/E.g...)
CHS ARIEL'S HTML LINKS PROGRAMMING:
COMPUTER HARDWARE SERVICING BANK ACCOUNT CONTROL SYSTEM
INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS MACHINES
INTERNATIONAL SPACE STATION HD LIVE
Mozilla Firefox, UC Browser, Safari, e.g...Browsers
HIGHEST EDUCATIONAL BACKGROUND:
Computer Hardware Servicing at University of Global site for Information Technology Studies Peñafrancia Ave. & Abella Street Brgy. Abella Naga City Camarines Sur Region V Philippines.
GLOBAL IT SITE/LOCATION:
University of Global site for Infomation Technology Studies Philippine Nationwide Branches/GLOBAL IT Los Angeles USA (Private Management).
PROFESSIONAL SKILLS, ACHIEVEMENT AND WORK EXPERIENCED/CAREER:
*SK Chairman at LGU of Brgy. Salvacion Pasacao CamSur (2007-2010).
*Former IEEE Technical Support at Atlantic Bakery (Chinese IEEE Components + Computer & Machineries Technical Support/Specialist).
*Former IT/Graphic Artist at Olivan Home Depot.
*Customer Service Representative at Sutherland Global Services Cam Sur Site.
GOVERNMENT ELIGIBILITY:
None Prof. Civil Service (2007-2010 SK Chairman at LGU of Pasacao).
CURRENTLY CAREER/NETWORKING JOB:
*Electricity Particles Physicist and IT Specialist (Computer Science Scientist/IEEE Computer Society)
CURRENTLY HOME BASE JOB AND PROFESSIONAL SKILLS/PRIVATE CAREERS:
*CSS, HTML/Java Script Programming (Computer Software), Website Builder and Php. Nationwide/International Projects Provider.
GOVERNMENT AGENCIES:
Information Technology, Advanced Science & technology Philippine Government Agencies/More!
Basic hand tools (Electronics Technology) - SlideSharehttps://www.slideshare.net › basic-hand-t...19 Jun 2014 · Basic hand tools for Electronics Technology. ...
BASIC HAND TOOLS Driving tools Soldering tools Slicing Tools Boring tools Cutting Tools ...CHS Electronics - Wikipediahttps://en.wikipedia.org › wiki › CHS_El...
CHS Electronics is a former multinational distributor of microcomputer products, personal computers, peripherals, networking products, and software. It was based ...
DescriptionHistoryMergersDemisebasic and common competencies chs nc ii.docx | Competence (Human Resources) | Electronics - Scribdhttps://www.scribd.com › document › ba...
BASIC COMPETENCIES. (18 hours) Units of Competency Module Title Learning Outcomes Nominal Duration. 1. Participate in workplace communication.Rating5.0 (1)VIDEOS
- YouTube · Make it mech3:18Basic Electronic components | How to and why to use electronics tutorialAug 14, 2017YouTube · Michel van Biezen4:10Electrical Engineering: Basic Concepts (2 of 7) Basic Circuit ElementsOct 21, 2015YouTube · CHS_Electronics20:06CHS Electronics Logo Project Full Build PC0-100144Nov 22, 2017YouTube · nptelhrd56:23Lecture - 1 Introduction to Basic ElectronicsJan 22, 2008YouTube · John Cimbala6:26Basic Electronics Example ProblemsJun 20, 2013
Computer Network Types
Generally, networks are distinguished based on their geographical span. A network can be as small as distance between your mobile phone and its Bluetooth headphone and as large as the internet itself, covering the whole geographical world,
Personal Area Network
A Personal Area Network (PAN) is smallest network which is very personal to a user. This may include Bluetooth enabled devices or infra-red enabled devices. PAN has connectivity range up to 10 meters. PAN may include wireless computer keyboard and mouse, Bluetooth enabled headphones, wireless printers and TV remotes.
For example, Piconet is Bluetooth-enabled Personal Area Network which may contain up to 8 devices connected together in a master-slave fashion.
Local Area Network
A computer network spanned inside a building and operated under single administrative system is generally termed as Local Area Network (LAN). Usually,LAN covers an organization’ offices, schools, colleges or universities. Number of systems connected in LAN may vary from as least as two to as much as 16 million.
LAN provides a useful way of sharing the resources between end users.The resources such as printers, file servers, scanners, and internet are easily sharable among computers.
LANs are composed of inexpensive networking and routing equipment. It may contains local servers serving file storage and other locally shared applications. It mostly operates on private IP addresses and does not involve heavy routing. LAN works under its own local domain and controlled centrally.
LAN uses either Ethernet or Token-ring technology. Ethernet is most widely employed LAN technology and uses Star topology, while Token-ring is rarely seen.
LAN can be wired,wireless, or in both forms at once.
Metropolitan Area Network
The Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) generally expands throughout a city such as cable TV network. It can be in the form of Ethernet,Token-ring, ATM, or Fiber Distributed Data Interface (FDDI).
Metro Ethernet is a service which is provided by ISPs. This service enables its users to expand their Local Area Networks. For example, MAN can help an organization to connect all of its offices in a city.
Backbone of MAN is high-capacity and high-speed fiber optics. MAN works in between Local Area Network and Wide Area Network. MAN provides uplink for LANs to WANs or internet.
Wide Area Network
As the name suggests,the Wide Area Network (WAN) covers a wide area which may span across provinces and even a whole country. Generally, telecommunication networks are Wide Area Network. These networks provide connectivity to MANs and LANs. Since they are equipped with very high speed backbone, WANs use very expensive network equipment.
WAN may use advanced technologies such as Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM), Frame Relay, and Synchronous Optical Network (SONET). WAN may be managed by multiple administration.
Internetwork
A network of networks is called an internetwork, or simply the internet. It is the largest network in existence on this planet.The internet hugely connects all WANs and it can have connection to LANs and Home networks. Internet uses TCP/IP protocol suite and uses IP as its addressing protocol. Present day, Internet is widely implemented using IPv4. Because of shortage of address spaces, it is gradually migrating from IPv4 to IPv6.
Internet enables its users to share and access enormous amount of information worldwide. It uses WWW, FTP, email services, audio and video streaming etc. At huge level, internet works on Client-Server model.
Internet uses very high speed backbone of fiber optics. To inter-connect various continents, fibers are laid under sea known to us as submarine communication cable.
Internet is widely deployed on World Wide Web services using HTML linked pages and is accessible by client software known as Web Browsers. When a user requests a page using some web browser located on some Web Server anywhere in the world, the Web Server responds with the proper HTML page. The communication delay is very low.
Internet is serving many proposes and is involved in many aspects of life. Some of them are:
- Web sites
- Instant Messaging
- Blogging
- Social Media
- Marketing
- Networking
- Resource Sharing
- Audio and Video Streaming
Network LAN Technologies
Let us go through various LAN technologies in brief:
Ethernet
Ethernet is a widely deployed LAN technology.This technology was invented by Bob Metcalfe and D.R. Boggs in the year 1970. It was standardized in IEEE 802.3 in 1980.
Ethernet shares media. Network which uses shared media has high probability of data collision. Ethernet uses Carrier Sense Multi Access/Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) technology to detect collisions. On the occurrence of collision in Ethernet, all its hosts roll back, wait for some random amount of time, and then re-transmit the data.
Ethernet connector is,network interface card equipped with 48-bits MAC address. This helps other Ethernet devices to identify and communicate with remote devices in Ethernet.
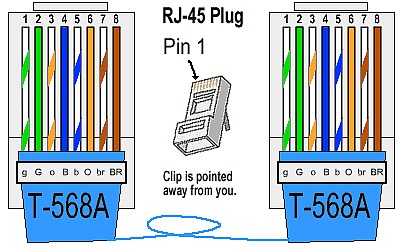
Traditional Ethernet uses 10BASE-T specifications.The number 10 depicts 10MBPS speed, BASE stands for baseband, and T stands for Thick Ethernet. 10BASE-T Ethernet provides transmission speed up to 10MBPS and uses coaxial cable or Cat-5 twisted pair cable with RJ-45 connector. Ethernet follows star topology with segment length up to 100 meters. All devices are connected to a hub/switch in a star fashion.
Fast-Ethernet
To encompass need of fast emerging software and hardware technologies, Ethernet extends itself as Fast-Ethernet. It can run on UTP, Optical Fiber, and wirelessly too. It can provide speed up to 100 MBPS. This standard is named as 100BASE-T in IEEE 803.2 using Cat-5 twisted pair cable. It uses CSMA/CD technique for wired media sharing among the Ethernet hosts and CSMA/CA (CA stands for Collision Avoidance) technique for wireless Ethernet LAN.
Fast Ethernet on fiber is defined under 100BASE-FX standard which provides speed up to 100 MBPS on fiber. Ethernet over fiber can be extended up to 100 meters in half-duplex mode and can reach maximum of 2000 meters in full-duplex over multimode fibers.
Giga-Ethernet
After being introduced in 1995, Fast-Ethernet could enjoy its high speed status only for 3 years till Giga-Ethernet introduced. Giga-Ethernet provides speed up to 1000 mbits/seconds. IEEE802.3ab standardize Giga-Ethernet over UTP using Cat-5, Cat-5e and Cat-6 cables. IEEE802.3ah defines Giga-Ethernet over Fiber.
Virtual LAN
LAN uses Ethernet which in turn works on shared media. Shared media in Ethernet create one single Broadcast domain and one single Collision domain. Introduction of switches to Ethernet has removed single collision domain issue and each device connected to switch works in its separate collision domain. But even Switches cannot divide a network into separate Broadcast domains.
Virtual LAN is a solution to divide a single Broadcast domain into multiple Broadcast domains. Host in one VLAN cannot speak to a host in another. By default, all hosts are placed into the same VLAN.
In this diagram, different VLANs are depicted in different color codes. Hosts in one VLAN, even if connected on the same Switch cannot see or speak to other hosts in different VLANs. VLAN is Layer-2 technology which works closely on Ethernet. To route packets between two different VLANs a Layer-3 device such as Router is required.
Network Services
Computer systems and computerized systems help human beings to work efficiently and explore the unthinkable. When these devices are connected together to form a network, the capabilities are enhanced multiple-times. Some basic services computer network can offer are.
Directory Services
These services are mapping between name and its value, which can be variable value or fixed. This software system helps to store the information, organize it, and provides various means of accessing it.
· Accounting
In an organization, a number of users have their user names and passwords mapped to them. Directory Services provide means of storing this information in cryptic form and make available when requested.
· Authentication &and Authorization
User credentials are checked to authenticate a user at the time of login and/or periodically. User accounts can be set into hierarchical structure and their access to resources can be controlled using authorization schemes.
· Domain Name Services
DNS is widely used and one of the essential services on which internet works. This system maps IP addresses to domain names, which are easier to remember and recall than IP addresses. Because network operates with the help of IP addresses and humans tend to remember website names, the DNS provides website’s IP address which is mapped to its name from the back-end on the request of a website name from the user.
File Services
File services include sharing and transferring files over the network.
· File Sharing
One of the reason which gave birth to networking was file sharing. File sharing enables its users to share their data with other users. User can upload the file to a specific server, which is accessible by all intended users. As an alternative, user can make its file shared on its own computer and provides access to intended users.
· File Transfer
This is an activity to copy or move file from one computer to another computer or to multiple computers, with help of underlying network. Network enables its user to locate other users in the network and transfers files.
Communication Services
Electronic mail is a communication method and something a computer user cannot work without. This is the basis of today’s internet features. Email system has one or more email servers. All its users are provided with unique IDs. When a user sends email to other user, it is actually transferred between users with help of email server.
· Social Networking
Recent technologies have made technical life social. The computer savvy peoples, can find other known peoples or friends, can connect with them, and can share thoughts, pictures, and videos.
· Internet Chat
Internet chat provides instant text transfer services between two hosts. Two or more people can communicate with each other using text based Internet Relay Chat services. These days, voice chat and video chat are very common.
· Discussion Boards
Discussion boards provide a mechanism to connect multiple peoples with same interests.It enables the users to put queries, questions, suggestions etc. which can be seen by all other users. Other may respond as well.
· Remote Access
This service enables user to access the data residing on the remote computer. This feature is known as Remote desktop. This can be done via some remote device, e.g. mobile phone or home computer.
Application Services
These are nothing but providing network based services to the users such as web services, database managing, and resource sharing.
· Resource Sharing
To use resources efficiently and economically, network provides a mean to share them. This may include Servers, Printers, and Storage Media etc.
· Databases
This application service is one of the most important services. It stores data and information, processes it, and enables the users to retrieve it efficiently by using queries. Databases help organizations to make decisions based on statistics.
· Web Services
World Wide Web has become the synonym for internet.It is used to connect to the internet, and access files and information services provided by the internet servers.
Overview
A system of interconnected computers and computerized peripherals such as printers is called computer network. This interconnection among computers facilitates information sharing among them. Computers may connect to each other by either wired or wireless media.
Classification of Computer Networks
Computer networks are classified based on various factors.They includes:
- Geographical span
- Inter-connectivity
- Administration
- Architecture
Geographically a network can be seen in one of the following categories:
- It may be spanned across your table, among Bluetooth enabled devices,. Ranging not more than few meters.
- It may be spanned across a whole building, including intermediate devices to connect all floors.
- It may be spanned across a whole city.
- It may be spanned across multiple cities or provinces.
- It may be one network covering whole world.
Components of a network can be connected to each other differently in some fashion. By connectedness we mean either logically , physically , or both ways.
- Every single device can be connected to every other device on network, making the network mesh.
- All devices can be connected to a single medium but geographically disconnected, created bus like structure.
- Each device is connected to its left and right peers only, creating linear structure.
- All devices connected together with a single device, creating star like structure.
- All devices connected arbitrarily using all previous ways to connect each other, resulting in a hybrid structure.
From an administrator’s point of view, a network can be private network which belongs a single autonomous system and cannot be accessed outside its physical or logical domain.A network can be public which is accessed by all.
Network Architecture
Computer networks can be discriminated into various types such as Client-Server,peer-to-peer or hybrid, depending upon its architecture.
- There can be one or more systems acting as Server. Other being Client, requests the Server to serve requests.Server takes and processes request on behalf of Clients.
- Two systems can be connected Point-to-Point, or in back-to-back fashion. They both reside at the same level and called peers.
- There can be hybrid network which involves network architecture of both the above types.
Computer systems and peripherals are connected to form a network.They provide numerous advantages:
- Resource sharing such as printers and storage devices
- Exchange of information by means of e-Mails and FTP
- Information sharing by using Web or Internet
- Interaction with other users using dynamic web pages
- IP phones
- Video conferences
- Parallel computing
- Instant messaging
Computer Network Toplogies
A Network Topology is the arrangement with which computer systems or network devices are connected to each other. Topologies may define both physical and logical aspect of the network. Both logical and physical topologies could be same or different in a same network.
Point-to-Point
Point-to-point networks contains exactly two hosts such as computer, switches or routers, servers connected back to back using a single piece of cable. Often, the receiving end of one host is connected to sending end of the other and vice-versa.
If the hosts are connected point-to-point logically, then may have multiple intermediate devices. But the end hosts are unaware of underlying network and see each other as if they are connected directly.
Bus Topology
In case of Bus topology, all devices share single communication line or cable.Bus topology may have problem while multiple hosts sending data at the same time. Therefore, Bus topology either uses CSMA/CD technology or recognizes one host as Bus Master to solve the issue. It is one of the simple forms of networking where a failure of a device does not affect the other devices. But failure of the shared communication line can make all other devices stop functioning.
Both ends of the shared channel have line terminator. The data is sent in only one direction and as soon as it reaches the extreme end, the terminator removes the data from the line.
Star Topology
All hosts in Star topology are connected to a central device, known as hub device, using a point-to-point connection. That is, there exists a point to point connection between hosts and hub. The hub device can be any of the following:
- Layer-1 device such as hub or repeater
- Layer-2 device such as switch or bridge
- Layer-3 device such as router or gateway
As in Bus topology, hub acts as single point of failure. If hub fails, connectivity of all hosts to all other hosts fails. Every communication between hosts, takes place through only the hub.Star topology is not expensive as to connect one more host, only one cable is required and configuration is simple.
Ring Topology
In ring topology, each host machine connects to exactly two other machines, creating a circular network structure. When one host tries to communicate or send message to a host which is not adjacent to it, the data travels through all intermediate hosts. To connect one more host in the existing structure, the administrator may need only one more extra cable.
Failure of any host results in failure of the whole ring.Thus, every connection in the ring is a point of failure. There are methods which employ one more backup ring.
Mesh Topology
In this type of topology, a host is connected to one or multiple hosts.This topology has hosts in point-to-point connection with every other host or may also have hosts which are in point-to-point connection to few hosts only.
Hosts in Mesh topology also work as relay for other hosts which do not have direct point-to-point links. Mesh technology comes into two types:
- Full Mesh: All hosts have a point-to-point connection to every other host in the network. Thus for every new host n(n-1)/2 connections are required. It provides the most reliable network structure among all network topologies.
- Partially Mesh: Not all hosts have point-to-point connection to every other host. Hosts connect to each other in some arbitrarily fashion. This topology exists where we need to provide reliability to some hosts out of all.
Also known as Hierarchical Topology, this is the most common form of network topology in use presently.This topology imitates as extended Star topology and inherits properties of bus topology.
This topology divides the network in to multiple levels/layers of network. Mainly in LANs, a network is bifurcated into three types of network devices. The lowermost is access-layer where computers are attached. The middle layer is known as distribution layer, which works as mediator between upper layer and lower layer. The highest layer is known as core layer, and is central point of the network, i.e. root of the tree from which all nodes fork.
All neighboring hosts have point-to-point connection between them.Similar to the Bus topology, if the root goes down, then the entire network suffers even.though it is not the single point of failure. Every connection serves as point of failure, failing of which divides the network into unreachable segment.
Daisy Chain
This topology connects all the hosts in a linear fashion. Similar to Ring topology, all hosts are connected to two hosts only, except the end hosts.Means, if the end hosts in daisy chain are connected then it represents Ring topology.
Each link in daisy chain topology represents single point of failure. Every link failure splits the network into two segments.Every intermediate host works as relay for its immediate hosts.
Hybrid Topology
A network structure whose design contains more than one topology is said to be hybrid topology. Hybrid topology inherits merits and demerits of all the incorporating topologies.
The above picture represents an arbitrarily hybrid topology. The combining topologies may contain attributes of Star, Ring, Bus, and Daisy-chain topologies. Most WANs are connected by means of Dual-Ring topology and networks connected to them are mostly Star topology networks. Internet is the best example of largest Hybrid topology
Computer Network Models
Networking engineering is a complicated task, which involves software, firmware, chip level engineering, hardware, and electric pulses. To ease network engineering, the whole networking concept is divided into multiple layers. Each layer is involved in some particular task and is independent of all other layers. But as a whole, almost all networking tasks depend on all of these layers. Layers share data between them and they depend on each other only to take input and send output.
Layered Tasks
In layered architecture of Network Model, one whole network process is divided into small tasks. Each small task is then assigned to a particular layer which works dedicatedly to process the task only. Every layer does only specific work.
In layered communication system, one layer of a host deals with the task done by or to be done by its peer layer at the same level on the remote host. The task is either initiated by layer at the lowest level or at the top most level. If the task is initiated by the-top most layer, it is passed on to the layer below it for further processing. The lower layer does the same thing, it processes the task and passes on to lower layer. If the task is initiated by lower most layer, then the reverse path is taken.
Every layer clubs together all procedures, protocols, and methods which it requires to execute its piece of task. All layers identify their counterparts by means of encapsulation header and tail.
OSI Model
Open System Interconnect is an open standard for all communication systems. OSI model is established by International Standard Organization (ISO). This model has seven layers:
· Application Layer: This layer is responsible for providing interface to the application user. This layer encompasses protocols which directly interact with the user.
· Presentation Layer: This layer defines how data in the native format of remote host should be presented in the native format of host.
· Session Layer: This layer maintains sessions between remote hosts. For example, once user/password authentication is done, the remote host maintains this session for a while and does not ask for authentication again in that time span.
· Transport Layer: This layer is responsible for end-to-end delivery between hosts.
· Network Layer: This layer is responsible for address assignment and uniquely addressing hosts in a network.
· Data Link Layer: This layer is responsible for reading and writing data from and onto the line. Link errors are detected at this layer.
· Physical Layer: This layer defines the hardware, cabling wiring, power output, pulse rate etc.
Internet Model
Internet uses TCP/IP protocol suite, also known as Internet suite. This defines Internet Model which contains four layered architecture. OSI Model is general communication model but Internet Model is what the internet uses for all its communication.The internet is independent of its underlying network architecture so is its Model. This model has the following layers:
· Application Layer: This layer defines the protocol which enables user to interact with the network.For example, FTP, HTTP etc.
· Transport Layer: This layer defines how data should flow between hosts. Major protocol at this layer is Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). This layer ensures data delivered between hosts is in-order and is responsible for end-to-end delivery.
· Internet Layer: Internet Protocol (IP) works on this layer. This layer facilitates host addressing and recognition. This layer defines routing.
· Link Layer: This layer provides mechanism of sending and receiving actual data.Unlike its OSI Model counterpart, this layer is independent of underlying network architecture and hardware.
Computer Network Security
During initial days of internet, its use was limited to military and universities for research and development purpose. Later when all networks merged together and formed internet, the data useds to travel through public transit network.Common people may send the data that can be highly sensitive such as their bank credentials, username and passwords, personal documents, online shopping details, or confidential documents.
All security threats are intentional i.e. they occur only if intentionally triggered. Security threats can be divided into the following categories:
· Interruption
Interruption is a security threat in which availability of resources is attacked. For example, a user is unable to access its web-server or the web-server is hijacked.
· Privacy-Breach
In this threat, the privacy of a user is compromised. Someone, who is not the authorized person is accessing or intercepting data sent or received by the original authenticated user.
· Integrity
This type of threat includes any alteration or modification in the original context of communication. The attacker intercepts and receives the data sent by the sender and the attacker then either modifies or generates false data and sends to the receiver. The receiver receives the data assuming that it is being sent by the original Sender.
· Authenticity
This threat occurs when an attacker or a security violator, poses as a genuine person and accesses the resources or communicates with other genuine users.
No technique in the present world can provide 100% security. But steps can be taken to secure data while it travels in unsecured network or internet. The most widely used technique is Cryptography.
Cryptography is a technique to encrypt the plain-text data which makes it difficult to understand and interpret. There are several cryptographic algorithms available present day as described below:
· Secret Key
· Public Key
· Message Digest
Secret Key Encryption
Both sender and receiver have one secret key. This secret key is used to encrypt the data at sender’s end. After the data is encrypted, it is sent on the public domain to the receiver. Because the receiver knows and has the Secret Key, the encrypted data packets can easily be decrypted.
Example of secret key encryption is Data Encryption Standard (DES). In Secret Key encryption, it is required to have a separate key for each host on the network making it difficult to manage.
Public Key Encryption
In this encryption system, every user has its own Secret Key and it is not in the shared domain. The secret key is never revealed on public domain. Along with secret key, every user has its own but public key. Public key is always made public and is used by Senders to encrypt the data. When the user receives the encrypted data, he can easily decrypt it by using its own Secret Key.
Example of public key encryption is Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA).
Message Digest
In this method, actual data is not sent, instead a hash value is calculated and sent. The other end user, computes its own hash value and compares with the one just received.If both hash values are matched, then it is accepted otherwise rejected.
Example of Message Digest is MD5 hashing. It is mostly used in authentication where user password is cross checked with the one saved on the server.
Physical Layer Introduction
Physical layer in the OSI model plays the role of interacting with actual hardware and signaling mechanism. Physical layer is the only layer of OSI network model which actually deals with the physical connectivity of two different stations. This layer defines the hardware equipment, cabling, wiring, frequencies, pulses used to represent binary signals etc.
Physical layer provides its services to Data-link layer. Data-link layer hands over frames to physical layer. Physical layer converts them to electrical pulses, which represent binary data.The binary data is then sent over the wired or wireless media.
Signals
When data is sent over physical medium, it needs to be first converted into electromagnetic signals. Data itself can be analog such as human voice, or digital such as file on the disk.Both analog and digital data can be represented in digital or analog signals.
· Digital Signals
Digital signals are discrete in nature and represent sequence of voltage pulses. Digital signals are used within the circuitry of a computer system.
· Analog Signals
Analog signals are in continuous wave form in nature and represented by continuous electromagnetic waves.
Transmission Impairment
When signals travel through the medium they tend to deteriorate. This may have many reasons as given:
· Attenuation
For the receiver to interpret the data accurately, the signal must be sufficiently strong.When the signal passes through the medium, it tends to get weaker.As it covers distance, it loses strength.
· Dispersion
As signal travels through the media, it tends to spread and overlaps. The amount of dispersion depends upon the frequency used.
· Delay distortion
Signals are sent over media with pre-defined speed and frequency. If the signal speed and frequency do not match, there are possibilities that signal reaches destination in arbitrary fashion. In digital media, this is very critical that some bits reach earlier than the previously sent ones.
· Noise
Random disturbance or fluctuation in analog or digital signal is said to be Noise in signal, which may distort the actual information being carried. Noise can be characterized in one of the following class:
o Thermal Noise
Heat agitates the electronic conductors of a medium which may introduce noise in the media. Up to a certain level, thermal noise is unavoidable.
o Intermodulation
When multiple frequencies share a medium, their interference can cause noise in the medium. Intermodulation noise occurs if two different frequencies are sharing a medium and one of them has excessive strength or the component itself is not functioning properly, then the resultant frequency may not be delivered as expected.
o Crosstalk
This sort of noise happens when a foreign signal enters into the media. This is because signal in one medium affects the signal of second medium.
o Impulse
This noise is introduced because of irregular disturbances such as lightening, electricity, short-circuit, or faulty components. Digital data is mostly affected by this sort of noise.
Transmission Media
The media over which the information between two computer systems is sent, called transmission media. Transmission media comes in two forms.
· Guided Media
All communication wires/cables are guided media, such as UTP, coaxial cables, and fiber Optics. In this media, the sender and receiver are directly connected and the information is send (guided) through it.
· Unguided Media
Wireless or open air space is said to be unguided media, because there is no connectivity between the sender and receiver. Information is spread over the air, and anyone including the actual recipient may collect the information.
Channel Capacity
The speed of transmission of information is said to be the channel capacity. We count it as data rate in digital world. It depends on numerous factors such as:
· Bandwidth: The physical limitation of underlying media.
· Error-rate: Incorrect reception of information because of noise.
· Encoding: The number of levels used for signaling.
Multiplexing
Multiplexing is a technique to mix and send multiple data streams over a single medium. This technique requires system hardware called multiplexer (MUX) for multiplexing the streams and sending them on a medium, and de-multiplexer (DMUX) which takes information from the medium and distributes to different destinations.
Switching
Switching is a mechanism by which data/information sent from source towards destination which are not directly connected. Networks have interconnecting devices, which receives data from directly connected sources, stores data, analyze it and then forwards to the next interconnecting device closest to the destination.
Switching can be categorized as:
Digital Transmission
Data or information can be stored in two ways, analog and digital. For a computer to use the data, it must be in discrete digital form.Similar to data, signals can also be in analog and digital form. To transmit data digitally, it needs to be first converted to digital form.
Digital-to-Digital Conversion
This section explains how to convert digital data into digital signals. It can be done in two ways, line coding and block coding. For all communications, line coding is necessary whereas block coding is optional.
Line Coding
The process for converting digital data into digital signal is said to be Line Coding. Digital data is found in binary format.It is represented (stored) internally as series of 1s and 0s.
Digital signal is denoted by discreet signal, which represents digital data.There are three types of line coding schemes available:
Uni-polar Encoding
Unipolar encoding schemes use single voltage level to represent data. In this case, to represent binary 1, high voltage is transmitted and to represent 0, no voltage is transmitted. It is also called Unipolar-Non-return-to-zero, because there is no rest condition i.e. it either represents 1 or 0.
Polar Encoding
Polar encoding scheme uses multiple voltage levels to represent binary values. Polar encodings is available in four types:
· Polar Non-Return to Zero (Polar NRZ)
It uses two different voltage levels to represent binary values. Generally, positive voltage represents 1 and negative value represents 0. It is also NRZ because there is no rest condition.
NRZ scheme has two variants: NRZ-L and NRZ-I.
NRZ-L changes voltage level at when a different bit is encountered whereas NRZ-I changes voltage when a 1 is encountered.
· Return to Zero (RZ)
Problem with NRZ is that the receiver cannot conclude when a bit ended and when the next bit is started, in case when sender and receiver’s clock are not synchronized.
RZ uses three voltage levels, positive voltage to represent 1, negative voltage to represent 0 and zero voltage for none. Signals change during bits not between bits.
· Manchester
This encoding scheme is a combination of RZ and NRZ-L. Bit time is divided into two halves. It transits in the middle of the bit and changes phase when a different bit is encountered.
· Differential Manchester
This encoding scheme is a combination of RZ and NRZ-I. It also transit at the middle of the bit but changes phase only when 1 is encountered.
Bipolar Encoding
Bipolar encoding uses three voltage levels, positive, negative and zero. Zero voltage represents binary 0 and bit 1 is represented by altering positive and negative voltages.
Block Coding
To ensure accuracy of the received data frame redundant bits are used. For example, in even-parity, one parity bit is added to make the count of 1s in the frame even. This way the original number of bits is increased. It is called Block Coding.
Block coding is represented by slash notation, mB/nB.Means, m-bit block is substituted with n-bit block where n > m. Block coding involves three steps:
- Division,
- Substitution
- Combination.
After block coding is done, it is line coded for transmission.
Analog-to-Digital Conversion
Microphones create analog voice and camera creates analog videos, which are treated is analog data. To transmit this analog data over digital signals, we need analog to digital conversion.
Analog data is a continuous stream of data in the wave form whereas digital data is discrete. To convert analog wave into digital data, we use Pulse Code Modulation (PCM).
PCM is one of the most commonly used method to convert analog data into digital form. It involves three steps:
- Sampling
- Quantization
- Encoding.
The analog signal is sampled every T interval. Most important factor in sampling is the rate at which analog signal is sampled. According to Nyquist Theorem, the sampling rate must be at least two times of the highest frequency of the signal.
Quantization
Sampling yields discrete form of continuous analog signal. Every discrete pattern shows the amplitude of the analog signal at that instance. The quantization is done between the maximum amplitude value and the minimum amplitude value. Quantization is approximation of the instantaneous analog value.
Encoding
In encoding, each approximated value is then converted into binary format.
Transmission Modes
The transmission mode decides how data is transmitted between two computers.The binary data in the form of 1s and 0s can be sent in two different modes: Parallel and Serial.
Parallel Transmission
The binary bits are organized in-to groups of fixed length. Both sender and receiver are connected in parallel with the equal number of data lines. Both computers distinguish between high order and low order data lines. The sender sends all the bits at once on all lines.Because the data lines are equal to the number of bits in a group or data frame, a complete group of bits (data frame) is sent in one go. Advantage of Parallel transmission is high speed and disadvantage is the cost of wires, as it is equal to the number of bits sent in parallel.
Serial Transmission
In serial transmission, bits are sent one after another in a queue manner. Serial transmission requires only one communication channel.
Serial transmission can be either asynchronous or synchronous.
Asynchronous Serial Transmission
It is named so because there’is no importance of timing. Data-bits have specific pattern and they help receiver recognize the start and end data bits.For example, a 0 is prefixed on every data byte and one or more 1s are added at the end.
Two continuous data-frames (bytes) may have a gap between them.
Synchronous Serial Transmission
Timing in synchronous transmission has importance as there is no mechanism followed to recognize start and end data bits.There is no pattern or prefix/suffix method. Data bits are sent in burst mode without maintaining gap between bytes (8-bits). Single burst of data bits may contain a number of bytes. Therefore, timing becomes very important.
It is up to the receiver to recognize and separate bits into bytes.The advantage of synchronous transmission is high speed, and it has no overhead of extra header and footer bits as in asynchronous transmission.
Privacy Policy